aptのデバッグオプションの話
はじめに
今日もせっせとlinuxマシンを情報シス業務で日夜触りまくっているネバー・フレンズ・Tです。 今回はみんな大好きUbuntu/Debian系のaptコマンドのデバッグの仕方についてちょこっと書いてみます。
実はaptはデバッグしやすい
apt-get source aptして取ってこれるaptのC++のソースコードを眺めていると、ソースコードの要所要所でデバッグ用の仕掛けが入っていることに気が付きます。この仕掛けを利用すると、いろいろ気の利いたところでデバッグ出力をさせることができますので、なにかaptの問題に遭遇したらちょこっと試してみるのも良いかもしれません。
まずはaptの設定内容を見る
aptにどういった設定がなされているか?はデバッグ開始前に確認しておいたほうが良いです。こんな時に便利なコマンドとしてapt-config dumpがあります。
$ apt-config dump
APT "";
APT::Architecture "amd64";
APT::Build-Essential "";
APT::Build-Essential:: "build-essential";
APT::Install-Recommends "1";
APT::Install-Suggests "0";
APT::Sandbox "";
APT::Sandbox::User "_apt";
APT::Authentication "";
APT::Authentication::TrustCDROM "true";
APT::NeverAutoRemove "";
APT::NeverAutoRemove:: "^firmware-linux.*";
APT::NeverAutoRemove:: "^linux-firmware$";
...後略...
aptのソースコードでも、apt-config dumpで出てくるような形式の文字列でフラグのON/OFFを確認しています。
実際の例:
_config->FindB("Debug::pkgAcquire"...
なお、ソース中のこのフラグ確認部分ですが、オプションの名前については大文字小文字を無視した判定(stringcasecmp():apt-2.5.3/apt-pkg/contrib/strutl.cc)をしているので、大文字小文字が異なっていても、同じオプションとして扱われます。
apt updateの処理の様子を見る
次は試しにapt updateがどこから何を取ってくるか?を確認してみます。
まずはコマンドラインオプションである、--print-urisをつけると、その一部をうかがい知ることができます。
$ apt update --print-uris
'http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/InRelease' deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_InRelease 0
'http://deb.debian.org/debian-debug/dists/sid-debug/InRelease' deb.debian.org_debian-debug_dists_sid-debug_InRelease 0
'http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/testing/InRelease' deb.debian.org_debian_dists_testing_InRelease 0
'http://deb.debian.org/debian-debug/dists/testing-debug/InRelease' deb.debian.org_debian-debug_dists_testing-debug_InRelease 0
'http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/main/source/Sources.xz' deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_main_source_Sources 0
'http://deb.debian.
...後略...
こちらの出力の詳しいところはapt-private/private-download.ccにあります。http://で始まる部分は、Debianパッケージリポジトリのどこからデータをダウンロードしてくるかを表し、deb.debian.org...とある部分は、デフォルト設定ですと、/var/lib/apt/lists/deb.debian.org...+<圧縮形式に応じた拡張子>というファイル名に格納しますよという意味になります。
さらにaptのソースを眺めてると、apt updateで使えそうな、デバッグオプションである、Debug::pkgAcquireが見つかります。早速有効にして確認してみましょう。
$ sudo apt update -o Debug::pkgAcquire=true
Fetching http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/InRelease
to /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_InRelease
Queue is: http:deb.debian.org
Fetching http://deb.debian.org/debian-debug/dists/sid-debug/InRelease
to /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian-debug_dists_sid-debug_InRelease
Queue is: http:deb.debian.org
Fetching http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/testing/InRelease
to /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_testing_InRelease
Queue is: http:deb.debian.org
Fetching http://deb.debian.org/debian-debug/dists/testing-debug/InRelease
to /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian-debug_dists_testing-debug_InRelease
Queue is: http:deb.debian.org
0% [ヘッダの待機中です]Dequeuing /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_InRelease
Dequeued from http:deb.debian.org
Dequeuing /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_InRelease
Fetching gpgv:/var/lib/apt/lists/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_InRelease
to /var/lib/apt/lists/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_InRelease
Queue is: gpgv
ヒット:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian sid InRelease
0% [ヘッダの待機中です]Dequeuing /var/lib/apt/lists/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_InRelease
Dequeued from gpgv
Dequeuing /var/lib/apt/lists/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_InRelease
0% [ヘッダの待機中です]Dequeuing /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian-debug_dists_sid-debu
g_InRelease
Dequeued from http:deb.debian.org
Dequeuing /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian-debug_dists_sid-debug_InRelease
Fetching gpgv:/var/lib/apt/lists/deb.debian.org_debian-debug_dists_sid-debug_InRelease
to /var/lib/apt/lists/deb.debian.org_debian-debug_dists_sid-debug_InRelease
Queue is: gpgv
...後略...
実際にaptが何をどうダウンロードしているか?の様子が見えるようになりました。
Debug::pkgAcquire::Worker=trueでmethodとのやり取りを見る
aptは時間かかりそうな処理がforkされたプロセスによるモジュールにわけられている(methodと呼ばれてます)ので、モジュールとの通信を読みたくなることが出てくると思います。まずはapt updateについてhttp/gpgv/storeのmethodの動作をapt-2.5.3をちょっぴり解析して図に示してみます。
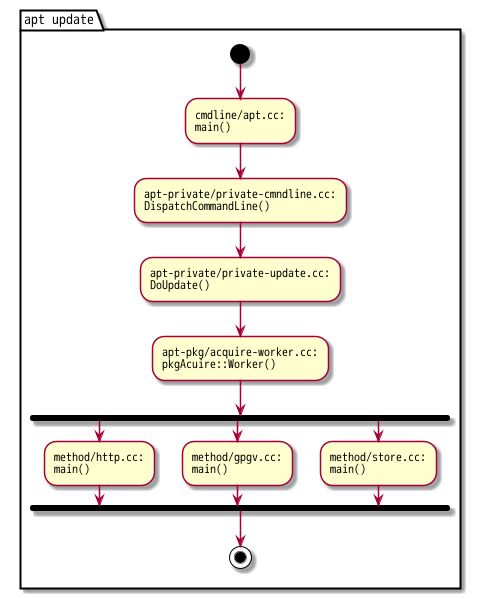
また、apt-2.5.3のmethodsのソースを見て、各methodsがどのような機能を持つか?を簡単な表にしてみます。
| method名 | 動作 | method 格納場所 | method ソースコード |
|---|---|---|---|
| http | http/https経由でデータをダウンロードしてくる | /usr/lib/apt/methods/http,https | methods/http.cc, basehttp.cc, connect.cc, rfc2553emu.cc |
| gpgv | ファイルに含まれる署名が正しいかを確認する | /usr/lib/apt/methods/gpgv | methods/gpgv.cc |
| store | ファイルの圧縮を扱う | /usr/lib/apt/methods/store | methods/store.cc |
| copy | ファイルのコピーを扱う | /usr/lib/apt/methods/copy | methods/copy.cc |
| ftp | anonymous ftpを扱う | /usr/lib/apt/methods/ftp | methods/ftp.cc, connect.cc, rfc2553emu.cc |
| cdrom | cdrom/dvdにパッケージリポジトリがある場合を扱う | /usr/lib/apt/methods/cdrom | methods/cdrom.cc |
| mirror | mirror先一覧リストを用いてパッケージリポジトリを変更する | /usr/lib/apt/methods/mirror, mirror+http, mirror+https, mirror+ftp, mirror+file, mirror+copy | methods/mirror.cc |
| file | ローカルマシンのディレクトリにパッケージリポジトリがある場合を扱う | /usr/lib/apt/methods/file | methods/file.cc |
| rsh | rsh/sshを使いリモートマシンのリポジトリにアクセス。ファイル一覧はリモート側でfindコマンド起動、データ転送はリモート側でddを起動し、標準入出力経由で入手する | /usr/lib/apt/methods/rsh,ssh | methods/rsh.cc |
さっそくpkgAcquire::Workerとmethodとのやりとりを見るためにDebug::pkgAcquire::Workerを追加で有効にしてみます。
$ sudo apt update -o Debug::pkgAcquire=true -o Debug::pkgAcquire::Worker=true
Starting method '/usr/lib/apt/methods/http'
<- http:100%20Capabilities%0aSend-URI-Encoded:%20true%0aSend-Config:%20true%0aPipeline:%20true%0aVersion:%201.2
Configured access method http
Version:1.2 SingleInstance:0 Pipeline:1 SendConfig:1 LocalOnly: 0 NeedsCleanup: 0 Removable: 0 AuxRequests: 0 SendURIEncoded: 1
Fetching http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/InRelease
to /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_InRelease
Queue is: http:deb.debian.org
Fetching http://deb.debian.org/debian-debug/dists/sid-debug/InRelease
to /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian-debug_dists_sid-debug_InRelease
Queue is: http:deb.debian.org
Fetching http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/testing/InRelease
to /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_testing_InRelease
Queue is: http:deb.debian.org
Fetching http://deb.debian.org/debian-debug/dists/testing-debug/InRelease
to /var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian-debug_dists_testing-debug_InRelease
Queue is: http:deb.debian.org
Starting method '/usr/lib/apt/methods/http'
<- http:100%20Capabilities%0aSend-URI-Encoded:%20true%0aSend-Config:%20true%0aPipeline:%20true%0aVersion:%201.2
Configured access method http
Version:1.2 SingleInstance:0 Pipeline:1 SendConfig:1 LocalOnly: 0 NeedsCleanup: 0 Removable: 0 AuxRequests: 0 SendURIEncoded: 1
-> http:601%20Configuration%0aConfig-Item:%20Acquire::Send-URI-Encoded=1%0aConfig-Item:%20APT::Architecture=amd64%0aConfig-Item:%20APT::Build-Essential::=build-essential%0aConfig-Item:%20APT::Install-Rec
...中略...
[処理中] <- http:102%20Status%0aMessage:%20debian.map.fastlydns.net%20%e3%81%b8%e6%8e%a5%e7%b6%9a%e3%81%97%e3%81%a6%e3%81%84%e3%81%be%e3%81%99%0aURI:%20http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/InRelease
<- http:102%20Status%0aMessage:%20debian.map.fastlydns.net%20(2a04:4e42:8c::644)%20%e3%81%b8%e6%8e%a5%e7%b6%9a%e3%81%97%e3%81%a6%e3%81%84%e3%81%be%e3%81%99%0aURI:%20http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/InRelease
<- http:102%20Status%0aMessage:%20Connected%20to%20debian.map.fastlydns.net%20(2a04:4e42:8c::644)%0aURI:%20http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/InRelease
<- http:102%20Status%0aMessage:%20%e3%83%98%e3%83%83%e3%83%80%e3%81%ae%e5%be%85%e6%a9%9f%e4%b8%ad%e3%81%a7%e3%81%99%0aURI:%20http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/InRelease
<- http:201%20URI%20Done%0aIMS-Hit:%20true%0aLast-Modified:%20Sat,%2003%20Sep%202022%2002:18:44%20+0000%0aFilename:%20/var/lib/apt/lists/partial/deb.debian.org_debian_dists_sid_InRelease%0aURI:%20http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/InRelease
...後略...
まず、Starting method '/usr/lib/apt/methods/〜'がどんなmethodをforkするか?を示しています。
さらに、<-(method側からaptへ)や、->(aptからmethodへ)で示される行が、pkgAcquire::Workerと各methodとの通信内容となります。フォーマットは
<通信の方向> <method名>:<MessageType>%20<ヘッダ>[:<電文の内容>]<CR><ヘッダ>[:<電文の内容]<CR>...
となります。
MessageTypeはaptのソース中、apt-pkg/acqure-worker.cc中にその一部ですが定義があります。
// Worker::RunMessage - Empty the message queue /*{{{*/
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
/* This takes the messages from the message queue and runs them through
the parsers in order. */
enum class APT_HIDDEN MessageType
{
CAPABILITIES = 100,
LOG = 101,
STATUS = 102,
REDIRECT = 103,
WARNING = 104,
URI_START = 200,
URI_DONE = 201,
AUX_REQUEST = 351,
URI_FAILURE = 400,
GENERAL_FAILURE = 401,
MEDIA_CHANGE = 403
};
あとは、apt-pkg/acqure-worker.cc中にハードコーディングされているMessageTypeとして、
| Message Type値 | 意味 | 定義場所 |
|---|---|---|
| 600 | 各methodにどんな指示を出すか? | apt-pkg/acquire-method.cc:pkgAcqMethod::Run() |
| 601 | 各methodにどんな設定で動かすか? | apt-pkg/acquire-method.cc:pkgAcqMethod::Run() |
があります。
例えば、
<- http:102%20Status%0aMessage:%20%e3%83%98%e3%83%83%e3%83%80%e3%81%ae%e5%be%85%e6%a9%9f%e4%b8%ad%e3%81%a7%e3%81%99%0aURI:%20http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/InRelease
の行ですが、意味としては、http methodからpkgAcquire::Worker方向に返却された通信で、MessageTypeはSTATUS、電文はStatusのみ、及び、Messageヘッダにそれぞれ入っていることを示します。さらに、Messageに入っている文字列はnkf --url-inputを使うと簡単にデコードできます。
$ sudo apt install nkf
$ echo '%20%e3%83%98%e3%83%83%e3%83%80%e3%81%ae%e5%be%85%e6%a9%9f%e4%b8%ad%e3%81%a7%e3%81%99%0a' |\
nkf --url-input
ヘッダの待機中です
というわけで、apt updateすると表示される「ヘッダの待機中です」という表示は実はhttp methodから来るメッセージでした。
これでmethodへどんな指示がapt側からされているか?あるいは、実際にどんなファイルをどういう設定で落とせと指示しているか?を知ることができます。
他のデバッグオプションと説明
基本的にデバッグオプションはman apt.confに記載があります。ソースも確認したければ、以下の方法でソースコードを検索することで他にも使えそうなデバッグオプションの一覧を検索できます。
$ apt-get source apt
$ ag 'Find..*Debug' | sed -s 's/^..*\(Debug::[^"][^"]*\)..*$/\1/g' | sort | uniq
Debug::APT::FTPArchive::Clean
Debug::APT::Progress::PackageManagerFd
...後略...
ここではapt-2.5.3のソースをもとにデバッグオプションを検索し、man apt.confで紹介されている数々のデバッグオプションとの差分を載せておきます。
man apt.confに記載がないデバッグオプション
| オプション名 | 対象コマンド名 | =trueの場合の説明 |
|---|---|---|
| Debug::APT::FTPArchive::Clean | apt-ftparchive | apt-ftparchive clean 時に、存在しないファイルをcache db から消去したあとの、新しくなったdbファイルの統計情報を表示する |
| Debug::Acquire::Retries | apt/apt-get | apt update等、debianパッケージリポジトリとの通信でリトライになったときにどの程度aptが待っているか?について表示する。 |
| Debug::Acquire::SrvRecs | apt/apt-get | Acquire::EnableSrvRecords=trueの時にapt update等で、RFC2782で定義されるDNSのSRVレコードに基づいてdebianパッケージリポジトリへネットワーク接続を実施するときの状況を表示する。 |
| Debug::Acquire::Transaction | apt/apt-get | apt update等でdebianパッケージリポジトリにアクセスしたあとどのようなファイル操作をローカル側でしているか?を表示する。 |
| Debug::AptMark::Minimize | apt-mark | apt-mark minimize-manualにて、どのように整理すべきパッケージを確認しにいったか?を出力。 |
| Debug::GetListOfFilesInDir | apt他 | aptに含まれる様々なコマンドで特定ディレクトリ配下のファイルを確認する操作にて、実際どういう判定を行ったか?を示す。具体的にはapt-pkg/contrib/fileutl.cc:GetListOfFilesInDir()の処理状況を表示。 |
| Debug::InstallProgress::Fancy | aptのみ | DPkg::Progress-Fancyがtrueの時、プログレスバーを表示するときの端末情報(端末サイズ等)をどう読み取ったか?を示す。 |
| Debug::Locking | apt他 | ファイルロックを取得する状況と結果がどうであったか?を示すようになる |
| Debug::SetupAPTPartialDirectory:: AssumeGood | apt/apt-get | /var/lib/apt/lists/partialのセットアップをしなくなる。 |
| Debug::acquire::progress | apt/apt-get | 1つのファイルについてどの程度の量をダウンロードしたか?を定期的に表示するようになる。 |
| Debug::pkgAcqArchive::NoQueue | apt/apt-get | パッケージのダウンロードのキューにダウンロード指示を積まなくなる。 |
| Debug::pkgCacheGen | apt/apt-get | パッケージキャッシュ(apt-cacheコマンド等で参照できる、aptコマンド群で内部利用される)がどのように構築されるか?を示す。 |
| Debug::pkgInitConfig | apt/apt-get | aptコマンドが内部でどんな設定になっているか?の一覧を表示してからaptの処理を実施するようになる。なお、このオプションはコマンドラインオプション-oが評価される以前に参照されるため、echo "Debug::pkgInitConfig true;" > dbg.cnf; sudo env APT_CONFIG=$(pwd)/dbg.cnf apt ...としなければ有効化できない。 |
man apt.confに記載があるが、未記載の機能を持つデバッグオプション
| オプション名 | 対象コマンド名 | =trueの場合の説明(補足) |
|---|---|---|
| Debug::pkgDPkgPM | apt/apt-get | man apt.confの通り、dpkgを呼び出すときのコマンドラインの内容を表示の他に、dpkgの実行そのものをスキップする能力がある。apt installやapt upgradeなど、一度dpkgが動いてしまうとシステムの状態が変わってしまい2回めのaptのテストができないような場合に、他のデバッグオプションとあわせて使うと便利。 |
man apt.confに記載があるが、利用できないデバッグオプション
apt-2.5.3のソースに実装がないため、実際には機能しないデバッグオプションを載せておきます。
| オプション名 |
|---|
| Debug::Acquire::http |
| Debug::Acquire::https |
| Debug::BuildDeps |
| Debug::pkgAcquire::RRed |
| Debug::sourceList |
これらフラグをいろいろtrueにしてみて、どういう出力が得られるか?を予め試して知っておくと、aptでピンチに至ったときにドヤ顔で「俺強ぇぇーっ」ができるときがあるかもしれません。
おわりに
謎の多いaptコマンドについて、デバッグオプションをtrueにすることでいろいろ調査できることを語ってみました。


